
Table of Contents
|
In the absence of facts, anyone's opinion is a good one...
|


|
Reporting and Measurement Table of Contents | |||
| ||||

| ||||
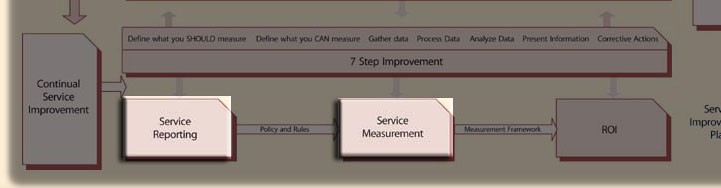
Introduction to Reporting and Measurement
Measurement and Reporting is a process within the Continual Service Improvement module of the ITIL Service Lifecycle.
| Objectives | Scope | Policies | Scaling | Concepts | Roles | Measuring | Processes | Appendix |
| As companies become increasingly adept at extracting and analyzing data, ironically, they often become slower to act. This "analysis paralysis" is a result of too great a focus on getting as much data as possible and not enough focus on developing strategies based on using the right data. The successful enterprise effectively extracts only the data required to make a decision and quickly turns that data into action. While the importance of analyzing the data cannot be underestimated and undervalued, it must be balanced by processes that quickly impart information to key decision-makers and allow for swift execution of strategy changes when the data uncovers the need. Although a fine line, there is a distinct difference in the results garnered from a "technology dependent" organization and a "technology-enabled" organization. |
![]()
How the Process Scales
![]()
Concepts
![]()
Roles and Responsibilities
![]()
| there is no single PM methodology because PM spans the complete management planning and control cycle. Think of it as a broad end-to-end union of solutions including three major purposes: collecting data, transforming and modeling the data into information, and web-reporting it to users and decision makers. Many of PM's component methodologies have existed for decades or have become recently popular, such as the balanced scorecard. Some of PM's components, such as activity-based cost management, are partially or crudely implemented in many organizations, and PM refines them so that they work in better harmony with PM's other components. Early adopters have deployed parts of PM, but few have deployed its full vision.
Gary Cokins, Performance Management – Making It Work |
| Term | Definition |
| Performance Management | The methodologies, metrics, processes, software tools, and systems that and manage the performance of an organization. |
| Strategy Maps | Depiction(s) which define strategic objectives and associated initiatives and action plans that support the organization’s vision and mission. |
| Strategic Objectives | the actions that an organization must complete—or at least make much progress toward—to achieve the organization’s mission. |
